Share this post:
Grenoble, France, September 9, 2019 – Microlight3D, a specialty manufacturer of high-resolution micro-scale 2D & 3D printing systems for industrial and scientific applications, today announces that the regenerative medicine project nAngioDerm, in which it is a partner, has been selected for funding in the amount of €747K ($822K). A consortium of research agencies from several countries will distribute the European funding; among them ANR, the French National Research Agency, which will underwrite Microlight3D’s participation.
nAngioDerm falls within the scope of EuroNanoMed3 (2016-2021), which supports multidisciplinary and translational research and innovation projects covering regenerative medicine, diagnostics and targeted delivery systems, under the European Horizon 2020 program.
Work on the project starts in this month and will run for 36 months.
“Microlight3D is very proud to be a partner in nAngioDerm, its first European research consortium,” said Denis Barbier, CEO of Microlight3D. “Collaborating with such high-level academic organizations on such a key health issue is further recognition of the value of our 3D microprinting technology for regenerative medicine applications. This project is a great opportunity in helping to further develop our micro-scale 3D printing systems for use in future health applications.”
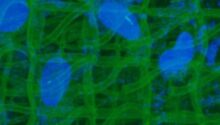
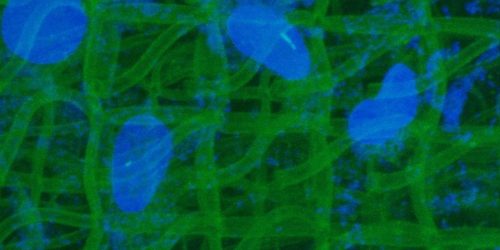
Microlight3D, one of five European partners collaborating on the nAngioDerm project, will contribute to bringing a solution to patients whose wounds from ulcers or major burns fail to heal. The partners will develop a new process and new products involving ion-release bio-materials which will promote angiogenesis for dermal regeneration. This demands skilled competences in tissue engineering, bio-active ions and cell-scaffold 3D-printing.
According to studies, the global burden for skin and subcutaneous diseases has increased rapidly over a 10-year period, with a prevalence of 605 million in year 2015 compared to 493 million in 2005. As many as 20 million people globally were reported in 2009 as living with acute wounds, as a result of surgery, or chronic skin ulcers. Wound care is associated with significant costs and has become a major challenge to healthcare systems worldwide. In a UK study on the health outcomes, resource implications and associated costs attributable to managing wounds in 2012/2013, the annual cost to the NHS (National Health Service) in managing wounds was estimated to be £4.5–5.1 billion. Strategies are being sought to improve the accuracy of diagnosis and healing rates.
Microlight3D will develop a 3D-printer and process dedicated to cell-scaffold application; a structure used in tissue engineering that provides support, enabling living tissue to regenerate itself and facilitate healing.
The lead partner, the Institute for Bioengineering in Catalonia (IBEC), will be responsible for bringing its research capacity in bio-active ions and bioengineering to the nAngioDerm project and coordinating the contributions of the other partners: the University of Ioannina, Greece, the Universitario Vall d’Hebron Hospital, Spain, the University of Grenoble, France and Microlight3D.
Microlight3D’s selection was based on its unique ability to develop 3D-printers that can print into biomaterials with sub-cell resolution and precision.
About the nAngioDerm project
nAngioDerm will develop nanostructured ion-release platforms and devices that promote the in-situ regeneration of damaged skin without the need of cells or growth factors. nAngioDerm’s innovative approach is based on the controlled release of bioactive ions (Zn2+, Ag+, Ca2+) from biodegradable polymeric nanocarriers, which will be developed using a nano-precipitation technique. These bioactive ions will promote cell recruitment and colonization and provide an antibacterial effect, as well as triggering the synthesis of angiogenic factors and extracellular matrix components that will facilitate wound healing. Depending on the type of skin injury, the ion-releasing nanocarriers will be combined with 3D printed collagen-based scaffolds as filling and guiding biomaterials for chronic wounds such as diabetic or pressure ulcers, or dispersed in a spray, based on a thermos-responsive collagen gel for acute wounds related to burns. The devices and platforms proposed here will be assessed in vitro and in suitable preclinical in vivo models as per EMA guidelines, bringing them to technology readiness level 4-5, close to clinical translation and market transferability stages. The comprehensive nAngioDerm project will equip researchers with a transferable and multidisciplinary skill set to enable them to adapt quickly to the challenging needs of the medtech sector and to afford them rapid ascent to key leadership positions in the field. In the long-term, the technologies developed will be implemented in other clinical areas, resulting in increased European-based knowledge, innovation, competitiveness and leadership in the field.
About Microlight3D
Microlight3D is a manufacturer of high-resolution micro-scale 2D & 3D printing systems. The company enables scientists and industrial researchers with new design needs to produce the most demanding precision micro parts in any geometric or organic shape with a flawless finish. By combining 2D & 3D microprinting techniques, Microlight3D offers customers more flexibility in creating larger complex parts. It aims to provide faster and more complex micro-fabrication systems for tomorrow’s applications. Microlight3D’s equipment is designed for application in microoptics, microfluidics, microrobotics, meta-materials, cell biology and microelectronics. Microlight3D was founded in 2016, following 15 years’ research and development of its 3D microprinting technology at Grenoble Alpes University (UGA). The company is located in Grenoble, France.